Diving into the Big Five Trait: Agreeableness
Margo Plater
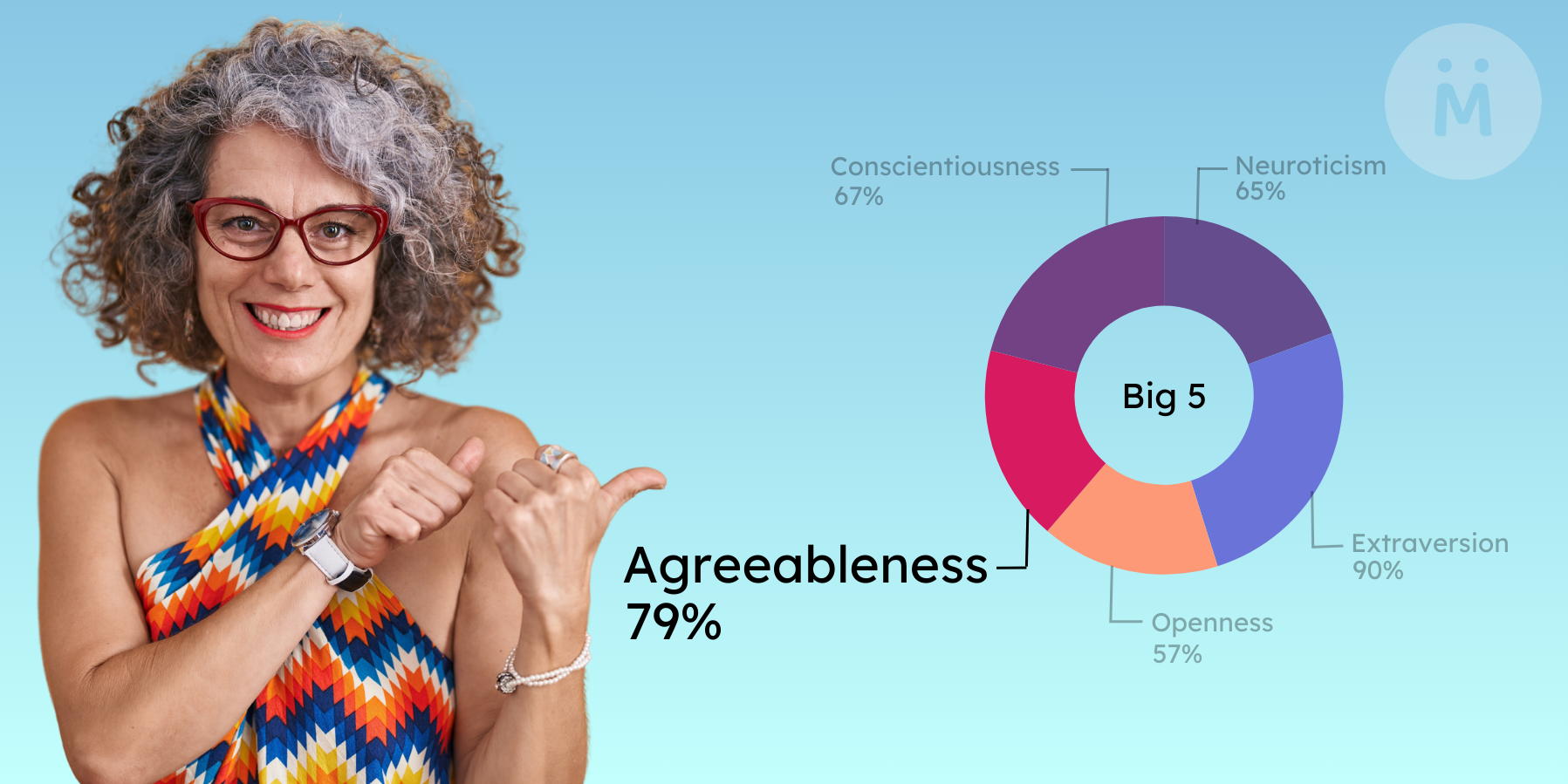
In the realm of psychometrics and psychology, the Big Five Personality Traits stand as a fundamental framework for understanding human behavior. Among these traits, agreeableness holds a distinct significance, offering insights into how individuals interact with others and navigate social situations. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the depths of this trait, unraveling its details and shedding light on its implications.
Understanding the Big Five Personality Traits
The Big Five Personality Traits, also known as the OCEAN model, is a theory that encompass five broad dimensions that show the variations in human personality. These traits include Openness to Experience, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Neuroticism, and, of course, Agreeableness. Each trait represents a spectrum along which individuals may fall, influencing their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors across diverse contexts. It states that personality can be described along five broad dimensions, each representing a spectrum of traits that capture the essence of individual differences. These dimensions provide a comprehensive lens through which to analyze and categorize various aspects of personality, offering valuable insights into human behavior across diverse contexts.
Brief Explanation of Each Trait
1. Openness
Openness to Experience reflects the extent to which individuals are receptive to new ideas, experiences, and perspectives. Those high in openness tend to be imaginative, curious, and intellectually adventurous, while those low in openness may prefer familiarity, routine, and tradition.
Conscientiousness pertains to the degree of organization, responsibility, and self-discipline exhibited by individuals. High conscientiousness is characterized by traits such as diligence, reliability, and goal-directedness, whereas low conscientiousness may manifest as impulsivity, disorganization, and lack of follow-through.
3. Extraversion
Extraversion encompasses the propensity for social engagement, assertiveness, and positive emotionality. Extraverted individuals thrive in social settings, enjoying interactions with others and seeking out stimulating experiences, whereas introverted individuals may prefer solitude, reflection, and quieter activities.
4. Neuroticism
Neuroticism reflects the tendency to experience negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and vulnerability to stress. Individuals high in neuroticism may be prone to mood swings, worry, and emotional instability, whereas those low in neuroticism tend to exhibit emotional resilience and a stable sense of well-being.
Agreeableness encompasses attributes related to interpersonal warmth, empathy, and cooperation. Individuals high in this trait are compassionate, trusting, and considerate of others' needs, fostering harmonious relationships and collaborative endeavors. Conversely, those low in this trait may exhibit traits such as skepticism, competitiveness, and a tendency towards conflict.
Emphasis on the Role of Agreeableness
Among the Big Five traits, agreeableness holds particular significance in shaping personality dynamics and interpersonal relationships. It serves as a key determinant of how individuals navigate social interactions, express empathy, and contribute to the collective well-being of society. Individuals high in this trait are adept at fostering rapport, resolving conflicts, and building trust, thereby enriching both their personal and professional lives. By recognizing the pivotal role of this trait in shaping personality, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of human behavior and the dynamics of social interaction. Individuals high in agreeableness tend to be compassionate, empathetic, and cooperative, prioritizing the well-being of others and seeking to maintain social harmony. Conversely, those low in agreeableness may exhibit traits such as assertiveness, skepticism, and a propensity for conflict.
Implications of Agreeableness in Various Contexts
Professional Settings
In the realm of business and leadership, agreeableness influences managerial styles, team dynamics, and organizational culture. Leaders high in agreeableness prioritize fostering a supportive work environment, promoting open communication, and nurturing cohesive teams.
Interpersonal Relationships
Within interpersonal relationships, agreeableness shapes the quality of interactions, influencing communication patterns, conflict resolution strategies, and overall relational satisfaction. Partnerships characterized by mutual respect, empathy, and cooperation thrive in environments where agreeable traits are prominent.
Health and Well-being
Agreeableness exerts a profound impact on individuals' psychological well-being and physical health. Studies have shown that agreeable individuals experience lower levels of stress, greater psychological resilience, and enhanced immune function, highlighting the holistic benefits of nurturing agreeable traits.
The trait of agreeableness stands as a cornerstone of human personality, wielding immense influence over our social interactions, professional pursuits, and overall well-being. By gaining a deeper understanding of the dimensions of agreeableness and its implications across diverse contexts, we can cultivate greater self-awareness, foster meaningful connections, and embark on a path toward personal growth and fulfillment.
Agreeableness Defined
Agreeableness stands as a fundamental dimension of personality, encompassing traits related to interpersonal warmth, empathy, and cooperation. Individuals high in agreeableness exhibit a predisposition towards kindness, compassion, and harmonious social relations, while those low in agreeableness may display tendencies towards skepticism, assertiveness, and conflict.
High Agreeableness
Individuals high in agreeableness exhibit a remarkable capacity for empathy, cooperation, and altruism. They prioritize harmonious relationships, often fostering amicable environments conducive to collaboration and mutual understanding. Traits associated with high agreeableness include:
- Compassion: High agreeableness individuals demonstrate genuine concern for others' well-being, readily extending support and empathy in times of need.
- Cooperativeness: Collaboration comes naturally to those high in agreeableness, as they value teamwork and consensus-building.
- Flexibility: With a propensity for compromise and adaptability, they navigate interpersonal conflicts with grace and diplomacy.
Understanding these traits paves the way for profound personal growth, enabling individuals to cultivate richer connections, enhance communication skills, and foster a sense of communal harmony.
Low Agreeableness
Conversely, individuals low in agreeableness may encounter distinct challenges in their interpersonal dynamics and personal development journey. Characteristics associated with low agreeableness encompass:
- Assertiveness: Those low in agreeableness often prioritize personal goals and assert their needs, sometimes at the expense of harmonious relationships.
- Competitiveness: Driven by ambition and self-interest, they may engage in competitive behaviors, striving for individual success rather than collective well-being.
- Bluntness: Direct and straightforward communication may characterize interactions with individuals low in agreeableness, occasionally leading to conflicts or misunderstandings.
Despite these challenges, acknowledging and understanding one's disposition towards agreeableness lays the foundation for transformative self-awareness and growth.
Breaking Down the Sub-facets of Agreeableness
- Trust
Trust reflects an individual's willingness to believe in the honesty, integrity, and benevolence of others. Trusting individuals are inclined to give others the benefit of the doubt and form close, meaningful relationships based on mutual respect and reciprocity.
- Straightforwardness
Straightforwardness pertains to the sincerity and honesty with which individuals communicate their thoughts, feelings, and intentions. Straightforward individuals value transparency and authenticity in their interactions, avoiding deception or manipulation.
- Altruism
Altruism encompasses selfless concern for the well-being of others, characterized by acts of kindness, generosity, and empathy. Altruistic individuals derive fulfillment from helping others and contributing to the greater good of society, without expecting anything in return.
- Compliance
Compliance refers to the tendency to conform to social norms, rules, and expectations in order to maintain harmony and avoid conflict. Individuals high in compliance prioritize social cohesion and adherence to established conventions, seeking to uphold societal values and norms.
- Modesty
Modesty entails humility and a lack of pretension in one's self-assessment and interactions with others. Modest individuals downplay their own achievements and talents, showing respect for others' contributions and avoiding self-aggrandizement.
- Tender-mindedness
Tender-mindedness reflects sensitivity, compassion, and sympathy towards others' emotional experiences and suffering. Individuals high in tender-mindedness demonstrate empathy and understanding, offering support and comfort to those in need.
By dissecting the sub-facets of agreeableness, we gain an understanding of the part of this trait and its implications for individual behavior and social dynamics.
The Impact of Agreeableness on Personal Development
Agreeableness encapsulates traits such as altruism, empathy, and cooperation. Individuals scoring high in agreeableness tend to be compassionate, trusting, and considerate, fostering harmonious relationships and social cohesion. This trait fosters a positive outlook towards others, promoting collaboration and effective communication in personal and professional spheres.
Understanding how agreeableness influences individual growth is paramount. Individuals often exhibit higher levels of emotional intelligence, enabling them to navigate complex social dynamics with ease. Moreover, agreeableness correlates positively with job satisfaction, leadership effectiveness, and overall well-being.
Understanding Your Dominant Trait: A Catalyst for Growth
Upon identifying one's dominant trait, whether high or low agreeableness, the journey towards personal growth commences. Embracing one's disposition and leveraging it as a catalyst for self-improvement empowers individuals to:
- Assert Boundaries: Those low in agreeableness can learn to assert boundaries effectively, balancing assertiveness with empathy and fostering healthier interpersonal dynamics.
- Enhance Communication Skills: Whether through active listening or assertive expression, understanding one's agreeableness level facilitates the refinement of communication skills essential for fostering meaningful connections and resolving conflicts constructively.
How Understanding Agreeableness Can Lead to Knowing Yourself Better
Self-awareness is the cornerstone of personal development, and understanding one's level of agreeableness provides valuable insights into one's behavior and interactions. By recognizing their agreeableness disposition, individuals can identify strengths to leverage and areas for improvement.
- Practice Empathy: Empathy is a fundamental aspect of agreeableness. Cultivate empathy by actively listening to others, acknowledging their perspectives, and demonstrating genuine concern for their well-being. This can help your relationships as well as understanding where your true perspectives lay by understanding others.
- Develop Conflict Resolution Skills: Enhance conflict resolution skills to navigate disagreements constructively. Focus on finding mutually beneficial solutions, maintaining open communication, and understanding the underlying needs of all parties involved. If you are able to understand where someone else is coming from who disagrees with you, you can better understand the motive for your opinions.
- Promote Positive Communication: Foster agreeableness through positive communication techniques such as assertiveness, active listening, and respectful dialogue. Encourage open exchange of ideas while valuing diverse opinions and perspectives to become aware of all opinions to hone your own.
- Seek Feedback and Self-Reflection: Solicit feedback from peers, mentors, and supervisors to gain insights into areas of improvement. Engage in regular self-reflection to evaluate behaviors, attitudes, and interactions, fostering continuous growth and development.
The impact of agreeableness on personal development is profound. By embracing and nurturing agreeable traits, individuals can cultivate fulfilling relationships, foster effective communication, and embark on a journey of self-discovery and growth. Embrace agreeableness as a catalyst for personal and interpersonal success, and witness the transformative power it bestows upon your life.
Navigating Challenges Associated with High Agreeableness
In today's fast-paced and competitive world, possessing agreeable traits can be both a boon and a challenge. While agreeableness fosters harmonious relationships and social cohesion, it may also present hurdles that individuals need to overcome.
Potential Downsides of High Agreeableness
- Overcommitment and Burnout
Individuals with high levels of agreeableness may find themselves prone to overcommitting in an effort to please others. This tendency can lead to burnout as they struggle to meet the demands of others while neglecting their own needs and priorities.
- Difficulty Saying No
Highly agreeable individuals often have difficulty asserting themselves and saying no, even when it's necessary for their own well-being. This can result in them being taken advantage of or being unable to prioritize their own goals and interests.
- Conflict Avoidance
While avoiding conflict can contribute to maintaining peaceful relationships, excessive avoidance may lead to unresolved issues and underlying resentment. High agreeableness may cause individuals to shy away from addressing important issues, ultimately hindering personal and professional growth.
Strategies for Navigating Challenges
- Establish Boundaries
Learning to set boundaries is crucial for individuals with high agreeableness. By clearly defining their limits and priorities, they can avoid overcommitment and ensure that their own needs are met.
- Practice Assertiveness
Developing assertiveness skills empowers individuals to express their needs and opinions confidently while maintaining respect for others. Learning to say no when necessary is essential for preserving one's time and energy.
- Seek Compromise
While it's important to assert oneself, compromising and finding mutually beneficial solutions are also valuable skills. High agreeableness can be an asset in negotiation scenarios, where finding common ground is key.
Balancing Agreeableness with Other Traits
Assertiveness
Balancing agreeableness with assertiveness allows individuals to maintain harmonious relationships while advocating for their own needs and interests. Striking this balance fosters healthy communication and mutual respect.
Conscientiousness
Developing emotional intelligence through conscientiousness enables individuals to navigate social situations effectively, understanding their emotions and those of others. This skill complements agreeableness by facilitating empathetic communication and conflict resolution.
While high agreeableness can facilitate positive social interactions, it's essential for individuals to navigate its challenges effectively. By establishing boundaries, practicing assertiveness, and seeking compromise, individuals can harness the benefits of agreeableness while maintaining their well-being and achieving their goals.
Implementing Insights for Personal Development
The true essence of self-discovery lies in its application to personal development. Armed with insights garnered from the Big Five Personality Test, individuals embark on a journey of self-improvement characterized by:
- Reflection: Regular self-assessment and introspection enable individuals to track their progress, identify areas for growth, and adapt their behaviors accordingly.
- Practice: Implementing newfound insights into daily interactions and relationships fosters gradual but meaningful transformation, enriching both personal and professional spheres.
- Seeking Support: Leveraging resources such as therapy, coaching, or peer support networks can provide invaluable guidance and accountability on the path toward personal development.
In essence, understanding and embracing one's agreeableness level serves as a cornerstone for holistic personal growth, enriching relationships, fostering self-awareness, and nurturing a fulfilling life journey.
Practical Strategies for Cultivating Agreeableness in Everyday Life
In today's fast-paced and often contentious world, cultivating agreeableness is an essential skill that can lead to greater harmony and success in both personal and professional spheres. In this section, we'll explore practical strategies for fostering agreeableness in various aspects of life.
Developing Interpersonal Skills
- Active Listening
One of the most effective ways to demonstrate agreeableness is through active listening. This involves fully engaging with others during conversations, showing genuine interest in their perspectives, and refraining from interrupting or dominating the discussion. By actively listening, we validate others' experiences and foster a sense of mutual respect and understanding.
- Empathy Building
Empathy lies at the core of agreeableness. Cultivating empathy involves putting oneself in others' shoes, understanding their emotions, and responding with compassion. Practicing empathy allows us to forge deeper connections with others, resolve conflicts peacefully, and build a supportive network of relationships.
Promoting Collaboration in the Workplace
- Encouraging Open Communication
Creating an environment where open communication is valued fosters a culture of collaboration and mutual respect. Encourage team members to express their thoughts and ideas freely, without fear of judgment or retribution. By promoting transparent communication channels, we facilitate teamwork and collective problem-solving.
- Recognizing and Celebrating Diversity
Valuing diversity in the workplace is paramount to fostering agreeableness. Recognize and celebrate the unique perspectives, backgrounds, and experiences that each team member brings to the table. Embrace diversity as a strength, rather than a source of division, and foster an inclusive environment where everyone feels valued and respected.
Nurturing Agreeableness in Personal Relationships
- Practicing Forgiveness
Forgiveness is a cornerstone of agreeableness in personal relationships. Holding onto grudges or resentments only serves to create tension and hostility. Instead, practice forgiveness by letting go of past grievances and focusing on reconciliation and moving forward together.
- Expressing Gratitude
Expressing gratitude is a powerful way to cultivate agreeableness in personal relationships. Take the time to acknowledge and appreciate the kindness, support, and love that others extend towards you. Whether through words of thanks or acts of kindness in return, expressing gratitude strengthens bonds and fosters a positive emotional connection.
Key Takeaways
Agreeableness, as one of the Big Five personality traits, encompasses characteristics such as kindness, cooperation, and empathy. Individuals high in agreeableness tend to prioritize harmony in their interactions with others, making them valuable assets in both personal and professional settings. Embracing agreeableness fosters a collaborative environment where individuals can thrive collectively. Agreeable individuals excel in conflict resolution due to their empathetic nature and ability to find common ground. Rather than escalating conflicts, they seek mutually beneficial solutions, fostering a culture of understanding and cooperation within teams and communities. Agreeableness cultivates trust and rapport, essential components of successful relationships. By demonstrating genuine care and concern for others' well-being, individuals can establish strong connections based on mutual respect and empathy.
It is important to take time to reflect on your interactions with others and identify areas where you can incorporate more agreeable behaviors, such as active listening and empathy. Put yourself in others' shoes and strive to understand their perspectives and feelings. Empathy strengthens connections and fosters a sense of unity and cooperation. Build relationships based on mutual respect and cooperation, recognizing the unique strengths and contributions of each individual. Collaboration breeds innovation and drives collective success.
In conclusion, embracing and celebrating agreeableness is not only beneficial for personal fulfillment but also essential for driving success in all aspects of life. By prioritizing kindness, cooperation, and empathy, individuals can cultivate meaningful relationships, resolve conflicts constructively, and lead with compassion. Let us embark on this journey together, embracing our agreeableness and creating a brighter future filled with harmony and understanding.



