Understanding the Trait of Neuroticism
Margo Plater
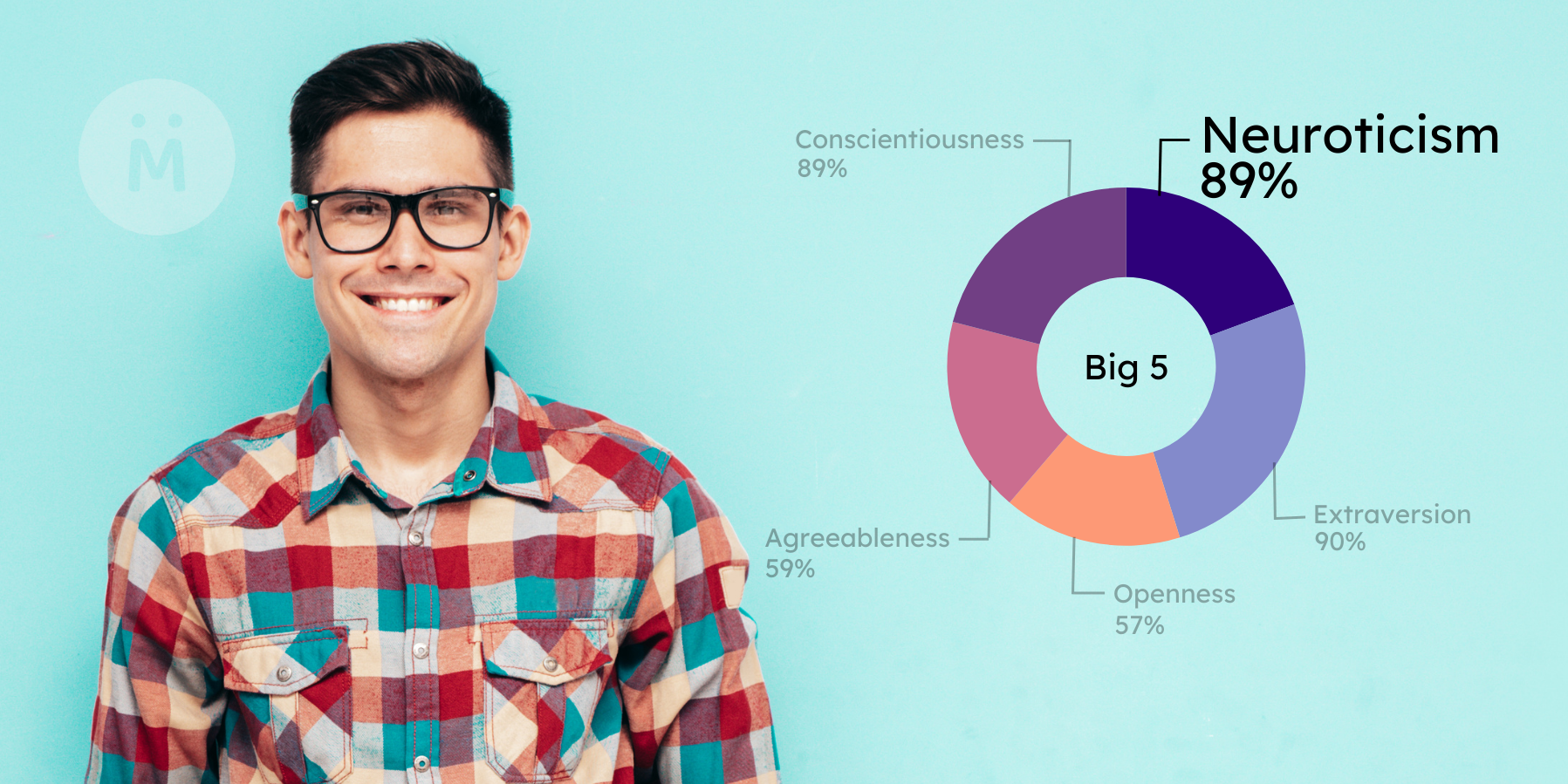
The Big Five Personality Traits
In the realm of personality psychology and psychometrics, the Big Five personality traits serve as a cornerstone for understanding individual differences. These traits, also known as the Five Factor Model (FFM), encompass five broad dimensions: openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Significance of Neuroticism
Neuroticism is important because it greatly affects how emotionally stable and mentally well a person is. Neuroticism refers to the tendency to experience negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and vulnerability to stress. People who are high in neuroticism tend to see normal situations as scary, which makes them feel more upset.
In this article, we delve into the intricate nature of neuroticism, exploring its manifestations, underlying mechanisms, and implications for personal and interpersonal functioning. By comprehensively understanding the trait of neuroticism, readers will gain valuable insights into its role in shaping behavior, relationships, and overall psychological functioning.
Understanding the Big Five Personality Traits
In comprehending human personality, the Big Five model serves as a pivotal theory and framework, offering profound insights into the intricacies of individual differences. Developed through extensive research in psychology, this model encapsulates five fundamental dimensions that encapsulate the spectrum of human personality.
Explanation of Each Trait
- Openness: This dimension reflects the extent to which an individual is open-minded, imaginative, and receptive to new ideas and experiences. Those high in openness tend to embrace novelty, creativity, and intellectual curiosity, while individuals low in openness may exhibit a preference for tradition, routine, and familiarity.
- Conscientiousness: Conscientiousness pertains to the degree of organization, responsibility, and self-discipline inherent in an individual's behavior. High conscientiousness is characterized by traits such as diligence, reliability, and goal-directedness, whereas low conscientiousness may manifest as impulsivity, disorganization, and lack of follow-through.
- Extraversion: Extraversion encompasses sociability, assertiveness, and positive emotionality. Individuals high in extraversion thrive in social settings, derive energy from interpersonal interactions, and tend to be outgoing and enthusiastic. Conversely, introverted individuals exhibit a preference for solitude, introspection, and subdued emotional expression.
- Agreeableness: Agreeableness reflects one's orientation towards interpersonal relationships, altruism, and cooperation. Those high in agreeableness demonstrate empathy, compassion, and a propensity for harmonious interactions, while individuals low in agreeableness may exhibit traits such as skepticism, competitiveness, and assertiveness.
- Neuroticism: Neuroticism pertains to emotional stability versus reactivity, capturing the propensity for experiencing negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and insecurity. High neuroticism is associated with heightened emotional volatility, sensitivity to stressors, and maladaptive coping mechanisms, whereas low neuroticism reflects emotional resilience, equanimity, and adaptive coping strategies.
Emphasis on the Role of Neuroticism in Personality
Of particular significance within the Big Five model is the dimension of neuroticism, which profoundly influences the manifestation of personality traits and behavioral tendencies. Individuals high in neuroticism are predisposed to heightened emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stressors, often experiencing intense negative emotions and exhibiting maladaptive coping strategies. This heightened susceptibility to negative affect can impact various domains of life, including relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
Neuroticism influences the way individuals perceive and respond to their environment, shaping their coping mechanisms, interpersonal interactions, and decision-making processes. Moreover, neuroticism interacts with other personality dimensions, amplifying or attenuating their effects on behavior and cognition. For instance, high neuroticism may exacerbate the impact of stressors on individuals high in conscientiousness, leading to heightened perfectionism or anxiety-driven procrastination.
The Nature of Neuroticism
Manifestations of Neuroticism
Neuroticism manifests across various domains of life, influencing how individuals perceive and respond to stressors. Common characteristics associated with neuroticism include heightened sensitivity to negative stimuli, a tendency towards self-doubt and rumination, and difficulty in coping with adversity. Individuals high in neuroticism may exhibit mood swings, emotional instability, and a propensity for worry and anxiety.
Impact on Personal Functioning
- Emotional Regulation
Neuroticism profoundly affects emotional regulation processes, influencing how individuals perceive, interpret, and manage their emotions. Being highly neurotic makes it hard to control negative emotions, which can make someone more likely to have depression or anxiety. Individuals high in neuroticism may struggle with emotion dysregulation, experiencing heightened emotional reactivity and difficulty in modulating emotional responses.
- Interpersonal Relationships
The trait of neuroticism exerts a significant influence on interpersonal relationships, shaping the dynamics and quality of social interactions. Individuals high in neuroticism may exhibit insecure attachment styles, characterized by fear of rejection and abandonment. Consequently, they may engage in maladaptive relationship behaviors such as excessive reassurance-seeking, jealousy, and emotional volatility, which can strain relationships and undermine intimacy.
Neuroticism Defined
Neuroticism as a Personality Trait
Neuroticism, one of the five fundamental dimensions of personality within the Big Five model, encompasses a spectrum of emotional stability versus reactivity. Neurotic individuals tend to experience heightened negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and insecurity when confronted with stress and life challenges. Conversely, those low in neuroticism exhibit greater emotional resilience and are less prone to intense fluctuations in mood.
What High Neuroticism Means
Being high in neuroticism entails a predisposition towards experiencing heightened emotional reactivity and vulnerability to stressors. Individuals with high neuroticism may find themselves easily overwhelmed by negative emotions, leading to a heightened sense of anxiety, worry, and rumination. They may also exhibit maladaptive coping strategies, such as avoidance or emotional outbursts, in response to perceived threats or setbacks.
- How Knowing These Traits Can Lead to Personal Growth
Awareness of one's high neuroticism can serve as a catalyst for personal growth and self-improvement. By recognizing their tendency towards negative emotional patterns, individuals can actively seek out strategies for managing stress, regulating emotions, and fostering resilience. This may involve mindfulness practices, cognitive-behavioral techniques, or seeking support from mental health professionals. Through self-awareness and proactive coping mechanisms, individuals can mitigate the detrimental effects of high neuroticism and cultivate greater emotional well-being.
What Low Neuroticism Means
Conversely, individuals low in neuroticism exhibit greater emotional stability and resilience in the face of adversity. They are less prone to experiencing intense negative emotions and it is easier to cope with life's challenges in a calm manner. Individuals with low neuroticism exhibit a more balanced emotional disposition, showing a tendency towards optimism, emotional flexibility, and adaptive coping strategies.
- How Knowing These Traits Can Lead to Personal Growth
Understanding one's low neuroticism can empower individuals to capitalize on their emotional strengths and cultivate further personal growth. People who have emotional stability are able to handle stress better. They can also stay positive during tough times. Additionally, they are able to build resilience when faced with obstacles. Moreover, recognizing their emotional resilience can instill confidence and a sense of agency, enabling individuals to pursue their goals with determination and perseverance.
Breaking Down the Sub-facets of Neuroticism
Neuroticism comprises several sub-facets that contribute to its overarching construct, each capturing distinct manifestations of emotional instability and reactivity. These sub-facets include:
Anxiety
Anxiety reflects a pervasive sense of worry, apprehension, and tension in response to perceived threats or uncertainties. Individuals high in anxiety may experience persistent feelings of nervousness, restlessness, and hypervigilance, which can interfere with daily functioning and impair quality of life.
Hostility
Hostility encompasses feelings of anger, resentment, and aggression towards others. Individuals high in hostility may exhibit a hostile attribution bias, perceiving ambiguous social cues as intentional slights or provocations, and reacting with hostility or aggression.
Depression
Depression entails a profound sense of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, often accompanied by feelings of worthlessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities. Individuals high in depression may experience persistent negative mood states and struggle to find pleasure or meaning in life.
Self-consciousness
Self-consciousness refers to an acute awareness and concern about one's perceived flaws, shortcomings, or social evaluation by others. Individuals high in self-consciousness may experience heightened self-criticism, social anxiety, and a tendency to compare themselves unfavorably to others.
Impulsiveness
Impulsiveness entails a propensity towards acting on urges or desires without sufficient forethought or consideration of consequences. Individuals high in impulsiveness may struggle with impulse control, leading to impulsive behaviors such as reckless decision-making, substance abuse, or binge eating.
Vulnerability
Vulnerability reflects a heightened sensitivity to stressors and a tendency towards emotional instability. Individuals high in vulnerability may experience intense emotional reactions to minor setbacks or perceived threats, leading to feelings of overwhelm, helplessness, and emotional dysregulation.
In essence, the sub-facets of neuroticism provide a nuanced understanding of the various emotional challenges and vulnerabilities that individuals may encounter within this personality dimension. By recognizing and addressing these sub-facets, individuals can cultivate greater self-awareness, develop adaptive coping strategies, and embark on a journey of personal growth and emotional well-being.
Leveraging the Big Five Personality Test for Self-Discovery
The Big Five Personality Test serves as a powerful tool for uncovering one's dominant traits, including neuroticism. By completing this assessment, individuals gain valuable insights into their unique personality profile, enabling deeper self-understanding and introspection.
Implementing Insights for Personal Development
Understanding one's dominant trait, such as neuroticism, is merely the first step towards personal growth. Implementing insights gleaned from the Big Five Personality Test requires intentional effort and commitment. Here's how to leverage this knowledge effectively:
Set Personal Goals
Identify areas for improvement based on your personality profile and set actionable goals to facilitate growth and development.
Practice Self-Reflection
Regularly reflect on your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors to gain insight into how your neurotic tendencies manifest in various aspects of your life.
Embrace Growth Opportunities
Be open to challenging yourself and stepping outside your comfort zone to foster personal growth and self-improvement.
Seek Feedback
Solicit feedback from trusted friends, family members, or mentors to gain additional perspective on areas where you can further develop and grow.
Neuroticism, though often viewed in a negative light, can serve as a catalyst for personal growth and self-discovery when approached with mindfulness and intentionality. By understanding the influence of neuroticism on personal development and leveraging insights from the Big Five Personality Test, individuals can embark on a transformative journey toward greater self-awareness, resilience, and fulfillment.
The Impact of Neuroticism on Personal Development
Exploring the Influence of Neuroticism on Individual Growth
Neuroticism, a fundamental trait in the Big Five Personality Model, plays a pivotal role in shaping individual growth and development. This trait encompasses tendencies towards anxiety, moodiness, worry, envy, jealousy, and loneliness. Understanding how neuroticism influences personal development is crucial for fostering a more enriching and fulfilling life journey.
Gaining insight into one's neurotic tendencies is a cornerstone of self-discovery. By comprehending the nuances of neuroticism, individuals can better grasp their thought patterns, emotional responses, and behavioral tendencies. This heightened self-awareness serves as a powerful tool for navigating life's challenges with resilience and adaptability.
Nurturing Neuroticism for Personal Growth
Contrary to common misconceptions, neuroticism can be harnessed as a catalyst for personal growth and self-improvement. Embracing neurotic traits involves acknowledging vulnerabilities and embracing them as opportunities for growth. Here are some actionable tips for nurturing neuroticism:
Embrace Vulnerability
Acknowledging vulnerabilities is the first step towards embracing neuroticism. Instead of viewing weaknesses as liabilities, consider them as avenues for growth and self-discovery.
Practice Mindfulness
Cultivating mindfulness can help individuals manage neurotic tendencies effectively. By staying present in the moment, individuals can gain better control over anxious thoughts and emotions, fostering a sense of inner peace and tranquility.
Seek Professional Guidance
Engaging in therapy or counseling can provide valuable insights and coping mechanisms for managing neuroticism. A qualified therapist can offer personalized strategies tailored to individual needs, facilitating meaningful progress toward personal development.
Cultivate Resilience
Building resilience is essential for navigating the ups and downs of life with grace and fortitude. Embrace setbacks as learning opportunities, and cultivate a growth mindset that fosters resilience in the face of adversity.
Overcoming Challenges Associated with Neuroticism
Understanding the Potential Downsides
Neuroticism, as a personality trait, can present individuals with a range of challenges in their daily lives. While it's important to acknowledge the diversity within neuroticism and its potential benefits, it's equally crucial to address the downsides associated with this trait.
Impact on Mental Well-being
One of the primary challenges of high neuroticism is its significant impact on mental well-being. Individuals with heightened neurotic tendencies often experience frequent and intense negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and stress. These emotions can interfere with their ability to function effectively in various domains of life, including work, relationships, and personal development.
Difficulty in Coping with Stressors
Moreover, individuals high in neuroticism tend to struggle more with coping mechanisms when faced with stressful situations. They may find it challenging to regulate their emotions, leading to heightened reactivity and maladaptive coping behaviors. This can further exacerbate feelings of distress and hinder their ability to navigate through life's inevitable challenges.
Increased Vulnerability to Health Issues
High levels of neuroticism have also been associated with an increased vulnerability to various health issues. Chronic stress resulting from neurotic tendencies can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses and diseases. Additionally, neuroticism has been linked to a higher prevalence of conditions such as cardiovascular disorders, gastrointestinal problems, and chronic pain syndromes.
Strategies for Effective Navigation
While neuroticism presents its share of challenges, there are several strategies that individuals can employ to navigate these difficulties while still embracing and maintaining their neurotic tendencies.
Developing Emotional Awareness and Regulation Skills
One effective approach is to focus on developing emotional awareness and regulation skills. By increasing their self-awareness and understanding of their emotional patterns, individuals can learn to recognize triggers and implement strategies to manage their reactions more effectively. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can be valuable tools in this process.
Cultivating Resilience and Adaptive Coping Strategies
Cultivating resilience is another key aspect of navigating challenges associated with neuroticism. Building resilience involves developing the ability to bounce back from setbacks and adversity, rather than being overwhelmed by them. This can be achieved through practices such as reframing negative thinking patterns, seeking social support, and engaging in activities that foster a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Seeking Professional Support and Guidance
In some cases, seeking professional support and guidance can be instrumental in managing neuroticism-related challenges. Mental health professionals, such as therapists and counselors, can provide individuals with tailored interventions and strategies to address specific issues they may be facing. This may include techniques for stress management, anxiety reduction, and improving overall well-being.
Embracing the Complexity of Personality
Rather than viewing neuroticism in isolation, it's essential to consider how it interacts with other personality traits and dimensions. For example, individuals high in neuroticism may also exhibit traits such as conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and openness to experience. Understanding the interplay between these traits can provide valuable insights into an individual's behavior, preferences, and strengths.
Cultivating Neuroticism
In today's dynamic world, fostering neuroticism is paramount for personal growth and exploration. Neuroticism, often misconstrued negatively, encompasses traits like anxiety, self-doubt, and emotional volatility. However, when channeled effectively, neuroticism can fuel creativity, resilience, and a drive for continuous improvement. Here, we present practical tips for cultivating neuroticism across various aspects of life.
Embracing Neuroticism in Everyday Activities
Embrace Uncertainty
Embrace uncertainty by reframing it as an opportunity for growth rather than a source of anxiety. Engage in activities that push you out of your comfort zone, such as trying new hobbies, traveling to unfamiliar places, or taking on challenging projects at work. Embracing uncertainty fosters adaptability and resilience, key components of neuroticism.
Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals manage and even embrace their neurotic tendencies. By staying present in the moment, individuals can gain better control over their thoughts and emotions, reducing the impact of anxiety and stress on their daily lives.
Set Realistic Goals
Set realistic, achievable goals that push you to grow without overwhelming you. Break larger goals down into smaller, manageable tasks, and celebrate each milestone along the way. This approach not only fuels a sense of accomplishment but also helps alleviate the fear of failure often associated with neuroticism.
Nurturing Neuroticism in Personal Relationships
Foster Vulnerability and Authenticity
Encourage open and honest communication in personal relationships, where individuals feel comfortable expressing their emotions and vulnerabilities without fear of judgment or rejection. Foster a sense of empathy and understanding, allowing individuals to connect on a deeper level and support each other through life's challenges.
Practice Active Listening
Practice active listening in personal relationships, where individuals genuinely listen to and empathize with each other's thoughts and feelings. Avoid judgment or criticism and instead focus on understanding and validating the other person's perspective. Active listening fosters trust and intimacy, strengthening personal connections and promoting emotional resilience.
Prioritize Self-Care
Prioritize self-care in personal relationships by setting aside time for relaxation, reflection, and rejuvenation. Engage in activities that nourish your mind, body, and soul, whether it's spending time in nature, practicing a hobby, or simply enjoying quality time with loved ones. Prioritizing self-care helps individuals recharge their emotional batteries and build resilience in the face of life's challenges.
By embracing neuroticism and implementing these practical tips in everyday life, professional settings, and personal relationships, individuals can foster growth, resilience, and exploration, unlocking their full potential in the process.
Key Takeaways
Neuroticism, a Big Five Personality Trait, is often associated with negative connotations, but it can also have positive aspects. Embracing neuroticism involves accepting and acknowledging these traits within yourself, rather than trying to suppress or hide them. By understanding the underlying motivations behind your neurotic tendencies, you can learn to harness them for personal growth and development.
Instead of viewing neuroticism as a downfall, we encourage you to reframe it as a valuable asset. Neurotic individuals are often highly conscientious and detail-oriented, traits that can be beneficial in many aspects of life, including work, relationships, and personal development. By embracing your neuroticism, you can leverage these strengths to achieve your goals and thrive in today's competitive world. Promoting well-being is important by embracing aspects of this trait and being aware of how it can impact you in everyday life to pivot and change mindsets to foster personal growth. In embracing this trait it is important to remember to, recognize your strengths, practice mindfulness, seek support, practice self-compassion, and set realistic goals.



